简介
CRD
建议先查看Kubernetes 控制器模型
Custom Resource
与custome resource 对应的词儿 是 built-in Kubernetes resources (like pods).
In the Kubernetes API, a resource is an endpoint that stores a collection of API objects of a certain kind
Custom ResourcesCustom resources can appear and disappear in a running cluster through dynamic registration
下文都假设自定义 一个 pod2 resource
CustomResourceDefinition
Spring 提供了扩展 xml 的机制,用来编写自定义的 xml bean ,例如 dubbo 框架,就利用这个机制实现了好多的 dubbo bean,比如 <dubbo:application> 、<dubbo:registry>。 spring ioc 启动时
- 会扫描带有类似@Component 注解的类,将它们纳入到ioc中
- 【spring系列】- Spring自定义标签工作原理自定义标签 会被转为一个BeanDefinition ,registerBeanDefinition 到ioc ,进而初始化为bean,并纳入到ioc 的管理,你可以在自己的类 @Autowire 使用这个registry 对象。
Pod 是kubernetes 的一个Resource ,会不会像spring 的BeanDefinition 一样有一个ResourceDefinition ,然后允许我们 自定义ResourceDefinition ? 答案是肯定的——CustomResourceDefinition。 custom resource 是自定义的,但描述custom resource的 CustomResourceDefinition 是built-in的,官网例子
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
# name must match the spec fields below, and be in the form: <plural>.<group>
name: crontabs.stable.example.com
spec:
xxx
Extending Kubernetes APIs with Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs)Custom resources definition (CRD) is a powerful feature introduced in Kubernetes 1.7 which enables users to add their own/custom objects to the Kubernetes cluster and use it like any other native Kubernetes objects.
| k8s | spring |
|---|---|
| k8s Resource | spring bean |
| CustomResourceDefinition | BeanDefinition |
| ResourceDefinition/code-generator ==> Generic APIServer | ioc ==> bean factory |
两相对比,还是很有味道的。
在nginx 中,你可以自定义 指令。比如笔者实现过一个 upsync 指令topsli/nginx-upsync-module-zk ,在nginx conf 中出现 upsync 指令时可以执行笔者的自定义逻辑。但自定义的指令 要和nginx 重新编译后 才可以生效,api server 可以不重启 支持 /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pod2s/{name} 么?
Custom controllers
对于k8s 来说,api server 只是将 pod2 这个resource crud 到 etcd 上,若要使其真正“干活儿” 还要实现 对应的Pod2 Controller
Custom ResourcesOn their own, custom resources simply let you store and retrieve structured data. It is only when combined with a controller that they become a true declarative API. A declarative API allows you to declare or specify the desired state of your resource and tries to match the actual state to this desired state. Here, the controller interprets the structured data as a record of the user’s desired state, and continually takes action to achieve and maintain this state.
基于声明式 API 的业务功能实现,往往需要通过控制器模式来“监视”API 对象的变化(比如,创建或者删除Pod2),然后以此来决定实际要执行的具体工作。
自定义custom controller 就有点 自定义 ansible module的意思。
实操——极客时间
来自极客时间 《深入剖析Kubernetes》
$ tree $GOPATH/src/github.com/<your-name>/pod2
.
├── controller.go
├── crd
│ └── pod2.yaml // custom resource definition 文件
├── example
│ └── example-pod2.yaml // 一个pod2.yaml 的例子
├── main.go
└── pkg
└── apis
└── pod2
├── register.go // 放置后面要用到的全局变量
└── v1
├── doc.go
├── register.go
└── types.go // 定一个pod2 到底有哪些字段
pod2 资源类型在服务器端的注册的工作,APIServer 会自动帮我们完成。但与之对应的,我们还需要让客户端也能“知道”pod2资源类型的定义。这就需要 pkg/apis/pod2/v1/register.go。
- 自定义资源类型的 API 描述,包括:组(Group)、版本(Version)等
- 自定义资源类型的对象描述,包括:Spec、Status 等
kubectl apply -f crd/pod2.yamlkubectl apply -f example/example-pod2.yaml
然后可以发现,单纯pod2 数据的crud 是没问题了,但crud 不是目的,我们希望能够根据 pod2 crud 做出反应,这就需要Controller 的协作了
-
使用 Kubernetes 提供的代码生成工具,为上面定义的pod2资源类型自动生成 clientset、informer和 lister。clientset 就是操作pod2 对象所需要使用的客户端。Informer,其实就是一个带有本地缓存和索引机制的、可以注册 EventHandler 的 client(三个 Handler(AddFunc、UpdateFunc 和 DeleteFunc)。通过监听到的事件变化,Informer 就可以实时地更新本地本地缓存,并且调用这些事件对应的 EventHandler
$ tree . ├── controller.go ├── crd │ └── pod2.yaml ├── example │ └── example-pod2.yaml ├── main.go └── pkg ├── apis │ └── pod2 │ ├── constants.go │ └── v1 │ ├── doc.go │ ├── register.go │ ├── types.go │ └── zz_generated.deepcopy.go └── client ├── clientset ├── informers └── listers - 编写 main 函数
- 编写自定义控制器的定义
- 编写控制器里的业务逻辑,APIServer 里保存的“期望状态”,“实际状态”来自 实际的集群,通过对比“期望状态”和“实际状态”的差异,完成了一次调协(Reconcile)的过程。
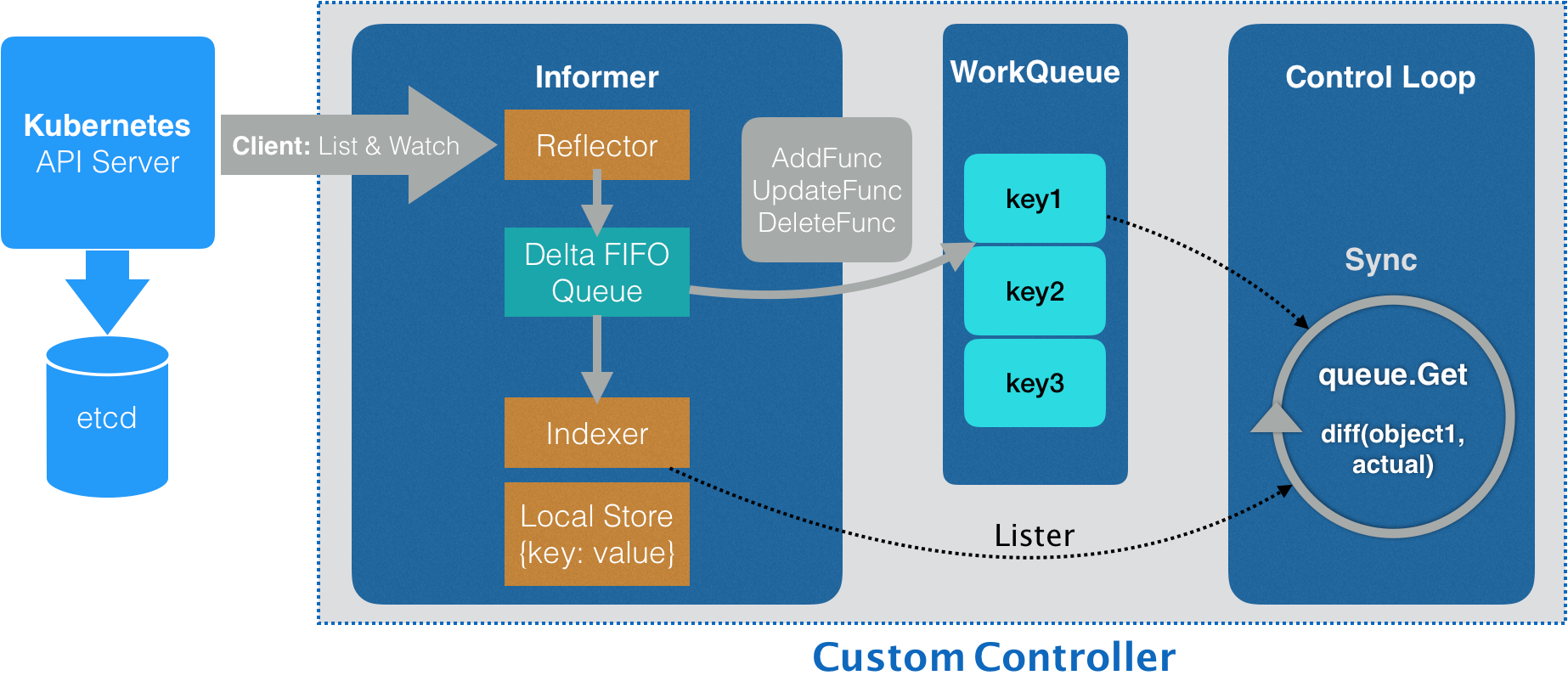
这套流程不仅可以用在自定义 API 资源上,也完全可以用在Kubernetes 原生的默认 API 对象上。
不管 built-in resource 还是 custom resource ,controller 不是 api server的一部分,自然也不用和 apiserver 一起启动,apiserver 只管crud etcd。
其它例子:一个自定义的crd(CustomResourceDefinition) 实现 resouer/k8s-controller-custom-resource
扩展API
自定义资源实际上是为了扩展kubernetes的API,向kubenetes API中增加新类型,可以使用以下三种方式:
- 修改kubenetes的源码,显然难度比较高,也不太合适
-
创建自定义API server并聚合到API中 Aggregated APIs are subordinate APIServers that sit behind the primary API server, which acts as a proxy.
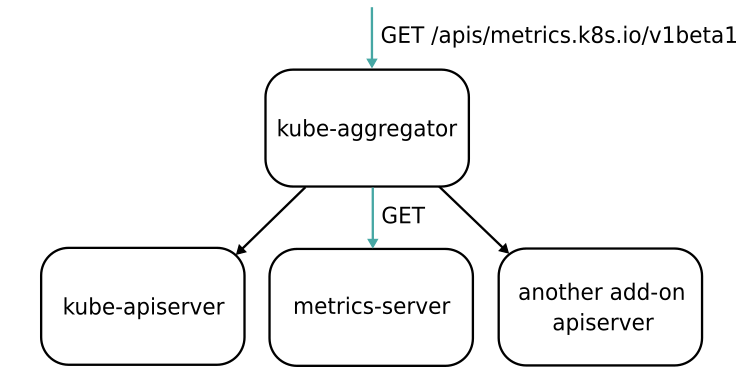
- 1.7以下版本编写TPR,kubernetes1.7及以上版本用CRD
使用CRD 有如下优势
- 你的API是否属于声明式的
- 是否想使用kubectl命令来管理
- 是否要作为kubenretes中的对象类型来管理,同时显示在kuberetes dashboard上
- 是否可以遵守kubernetes的API规则限制,例如URL和API group、namespace限制
- 是否可以接受该API只能作用于集群或者namespace范围
- 想要复用kubernetes API的公共功能,比如CRUD、watch、内置的认证和授权等
Kubernetes Deep Dive: Code Generation for CustomResources
实操——Ingress(未完成)
Ingress 背景及作用参见访问Kubernetes上的服务
Kubernetes Ingress(2)Controller源码分析未理解
Kubernetes Ingress Controller的使用介绍及高可用落地未读
另一种扩展——operator
Kubernetes Controller vs Kubernetes Operator?
The list of controller in the Control-plane,比如
- Deployment
- ReplicaSet
- StatefulSet
- DaemonSet
From the Google Search, I found out that there are K8s Operators such as
- etcd Operator
- Prometheus Operator
- kong Operators
All Operators use the controller pattern, but not all controllers are Operators. It’s only an Operator if it’s got: controller pattern + API extension + single-app focus.
Operator is a customized controller implement with CRD. It follow the same pattern with build-in controllers (i.e. watch, diff, action).
作者 believe the term “kubernetes operator” was introduced by the CoreOS people here
An Operator is a method of packaging, deploying and managing a Kubernetes application. A Kubernetes application is an application that is both deployed on Kubernetes and managed using the Kubernetes APIs and kubectl tooling.
An Operator is an application-specific controller that extends the Kubernetes API to create, configure and manage instances of complex stateful applications on behalf of a Kubernetes user. It builds upon the basic Kubernetes resource and controller concepts, but also includes domain or application-specific knowledge to automate common tasks better managed by computers.
So basically, a kubernetes operator is the name of a pattern that consists of a kubernetes controller that adds new objects to the Kubernetes API, in order to configure and manage an application, such as Prometheus or etcd. 为应用kubernetes 化而生的。
In one sentence: An operator is a domain specific controller.