简介
http://fishcried.com/ 有一个linux 网络的基础知识系列,要研读下
ip命令
我们知道经典的OSI七层网络模型,学要致用,要将其掺入到对linux网络命令的理解中。
我们知道网卡有mac地址和ip地址,分别用在链路层和网络层。打个比方,MAC地址像是我们的身份证,到哪都是那个样子;IP像是居住证,换了地方信息就要变了。政府机构同时给公民发身份证和居住证以便管理动态的社会,网络管理机构则通过给所有的上网设备同时分配MAC和IP达到这个目的。(mac地址是和位置无关的,所以是不可路由的)(这个比方来自知乎)是不是有点动静结合的意思。
一开始mac地址都是烧在网卡中的,后来则是可以动态设置(虚拟的网卡mac地址就更可以改变了)。网卡的ip地址和mac地址可变也没什么关系,因为交换机和路由器可以学习所连接网络pc的ip、mac和swtich/router的port的对应关系。网卡可以设置为混杂模式,这样一个网卡可以接受所有收到的数据包(即便数据包的目的ip地址不是该网卡的ip地址)。
iproute2是一个套件,包含的是一套命令,类似于docker,所有的docker操作命令以docker开头,就可以完成关于docker的所有操作。具体的子操作,则类似于”docker network xx”。
既然网络是分层的,那么理论上讲不同的ip命令负责不同层的事情。比如ip link (Data Link layer,所以叫ip link)负责第二层,ip address负责第三层。所以,当你想设置mtu时(肯定是第二层的事),你得找ip link。
较高版本的linux内核支持namespace,因此ip命令还可以设置某个namespace的网卡(实际上,我们通常在root namespace执行ip命令,root namespace可以“看见”所有的子namespace)。
通过man ip我们可以看到
ip link add link DEVICE [ name ] NAME
[ txqueuelen PACKETS ]
[ address LLADDR ] [ broadcast LLADDR ]
[ mtu MTU ]
type TYPE [ ARGS ]
TYPE := [ vlan | veth | vcan | dummy | ifb | macvlan | can | bridge]
这说明,ip命令不仅可以添加网卡,还可以添加网桥等网络设备。
brctl
写的挺好,都不忍心翻译
Software defined networking (SDN) is the current wave sweeping the networking industry. And one of the key enablers of SDN is virtual networking. While SDN and virtual networking are in vogue these days, the support for virtual networking is not a recent development. And Linux bridge has been the pioneer in this regard.(简述SDN、virtual networking、Linux Bridge之间的关系)
Virtual networking requires the presence of a virtual switch inside a server/hypervisor. Even though it is called a bridge, the Linux bridge is really a virtual switch and used with KVM/QEMU hypervisor. Linux Bridge is a kernel module, first introduced in 2.2 kernel (circa 2000). And it is administered using brctl command on Linux.
以下来自man btctl
The command brctl addbr <name> creates a new instance of the ethernet bridge. The network interface corresponding to the bridge will be called “name”.
The command brctl delbr <name> deletes the instance “name” of the ethernet bridge. The network interface corresponding to the bridge must be down before it can be deleted!
Each bridge has a number of ports attached to it. Network traffic coming in on any of these ports will be forwarded to the other ports transparently, so that the bridge is invisible to the rest of the network.
The command brctl addif <brname> <ifname> will make the interface “ifname” a port of the bridge “brname”. This means that all frames received on “ifname” will be processed as if destined for the bridge.
总的来说,就是使用brctl
- 可以查看所有的linux bridge,增加和删除linux bridge
- 针对一个linux bridge,可以将一个interface挂到bridge或移除,可以查看“挂到”上面的所有interface
- 每建一个网桥,都会建一个跟网桥同名的interface,并挂在网桥上面。
pipework
In the long run, Docker will allow complex scenarios, and Pipework should become obsolete.
Pipework唯一的官方文档https://github.com/jpetazzo/pipework/blob/master/README.md
pipework的主要功能就是容器网络的一些设置,容器以容器id(或name)标识,pipework内部会调用docker inspect获取容器的信息,进而对容器进行设置(其实就是对ip命令的一些封装(ip命令也可以操作netns的中的网络设备信息))。类比的说,pipework的作用相当于新版本docker的docker network和docker run --net xxx --ip xxx的组合。
ovs
brctl和ovs都有interface和port的概念,并且interface和port往往是一起设置的(将网卡连在某个port上嘛)
ovs的安装在centos上较为麻烦,需要将某些代码注释掉。
ovs-docker
wget https://github.com/openvswitch/ovs/raw/master/utilities/ovs-docker
iptables
从tomcat filter说起
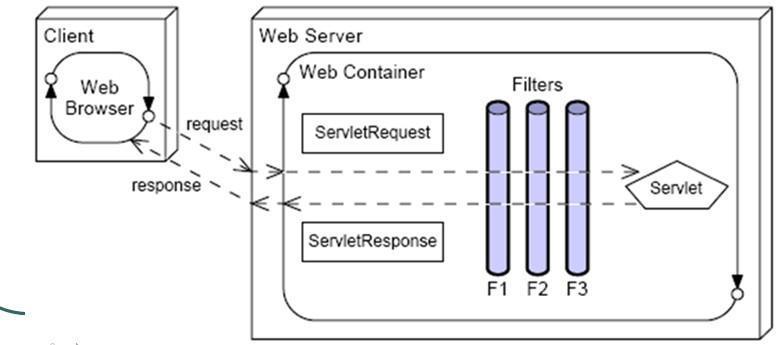
每次请求过来都会创建一个过滤器链(filterChain),并把待执行的servlet对象存放到过滤器链中。对于每个url,对应的filter个数都是不固定的,filterchain需要保存每个请求所对应的一个filter数组,以及调用到的filter的position,以便继续向下调用filter
tomcat filter ==> netfilter
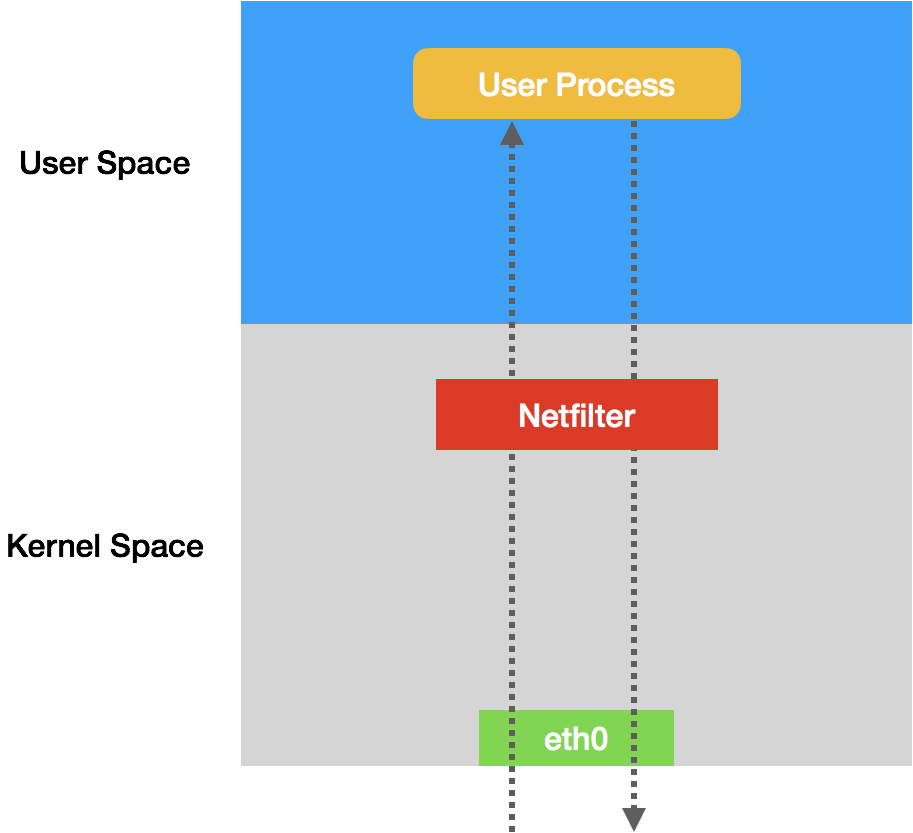
Netfilter 子系统的作用,就是 Linux 内核里挡在“网卡”和“用户态进程”之间的一道“防火墙”。
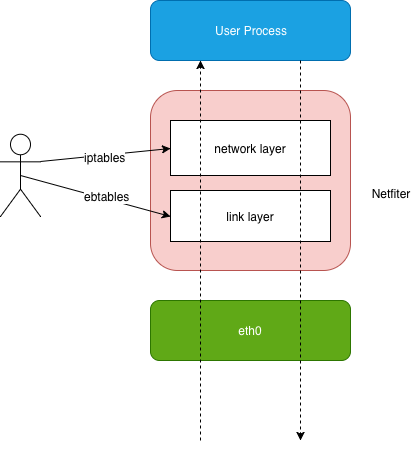
iptables 只是一个操作 Linux 内核 Netfilter 子系统的“界面”。链路层的“检查点”对应的操作界面叫作 ebtables。
| linux 网络协议栈 | http server | rpc server | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 操作界面 | iptables、ebtables | xml | 大部分框架为硬编码 |
| 拦截的最小单位 | rule | Filter | 根据框架有所不同,一般为Filter |
| 最小单位的上一层单位 | table | FilterChain | Filter 数组 |
| 再上一层单位 | Chain | ||
| 流向 | 有forward 和 upward 两种流向 | 只有upward 一种流向 | 只有upward 一种流向 |
| 路由 | 路由表 | Mapping | router |
笔者之前只是觉得 http server 与 rpc server 很像,但宽泛的说,网络协议栈与http server、rpc server 也是异曲同工。但我们学习 网络协议栈时,往往是从chain ==> table ==> rule 开始说。而http server 和 rpc server 则是从小到达 来表述。另一个显著地差异是,netfilter 有两种流向,chain的个数 也就更多,chain 可以形象的称之为“检查站”
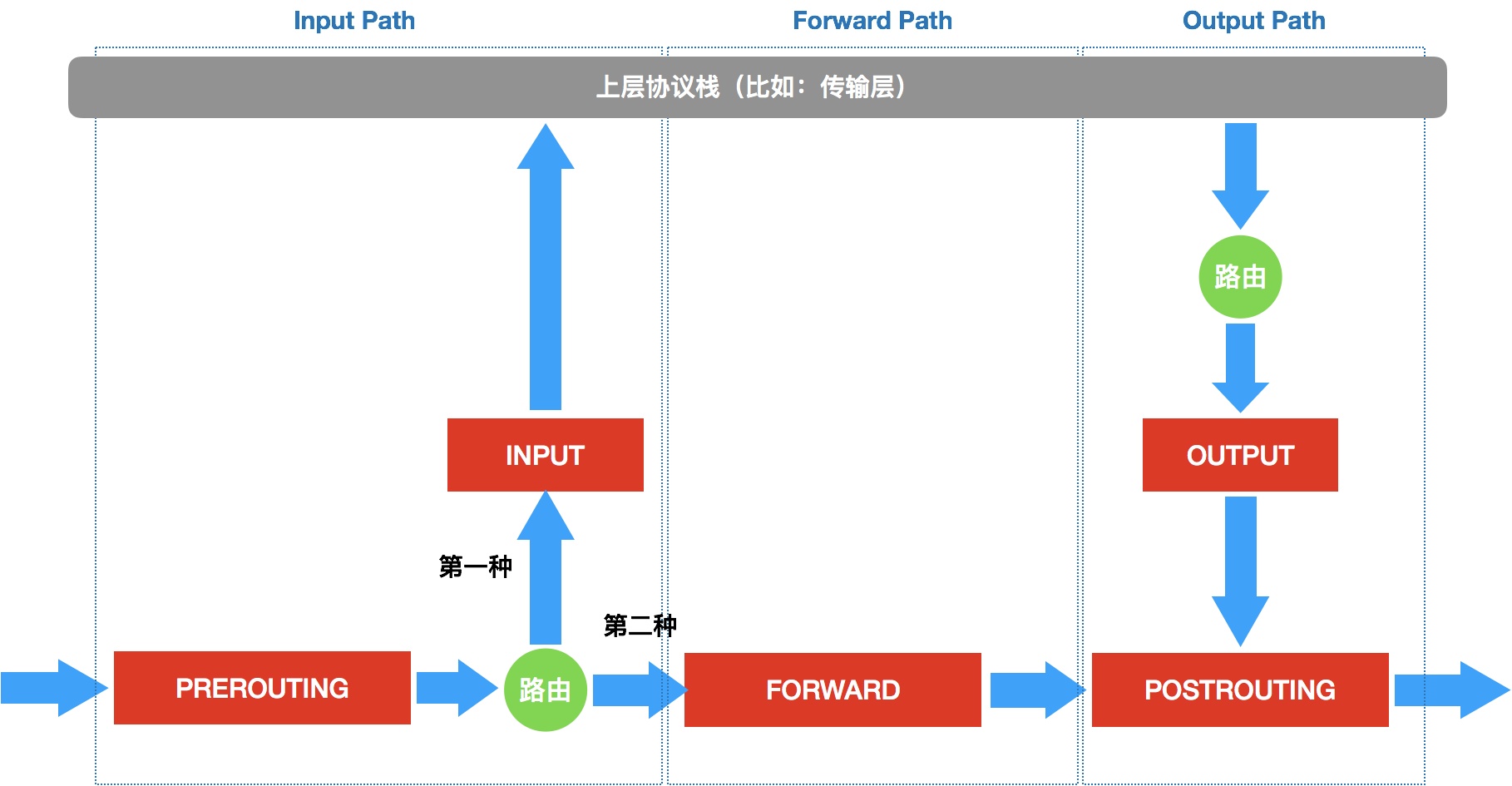
iptables 表的作用,就是在某个具体的“检查点”(比如Output)上,按顺序执行几个不同的检查动作(比如,先执行nat,再执行 filter)。
| 类比于快递站点 | |
|---|---|
| chain | 发货点、分拨中心、集散中心、营业点 |
| table | 入库、分拨、核对、安检 |
| rule | 比如入库,比如不接收xx的快递、不接收大于xx快递等 |
操作
iptbales -L -vn –line-number
iptables -D INPUT 7
iptables -D FORWARD 4
这样按序号删规则很方便
- iptables 是 按rules 来办事的,这些规则分别指定了源地址、目的地址、传输协议等,并按数据包与规则是否匹配采取accept、reject、drop等action
- rule 通常不只一个,所以多个rule 组成一个链,链分为自定义链和默认链
-
根据链生效位置、以及host是否开始ip_forward的不同
- 到本机某进程的报文 prerouting–> input
- 开启转发功能时,由本机转发的报文 prerouting –> forward ==> postrouting
- 由本机的某进程发出报文 output –> postrouting
-
自定义链允许我们以自定义名称组织相关的规则,要被默认链引用,才可以生效
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination cali-INPUT all -- anywhere anywhere /* cali:Cz_u1IQiXIMmKD4c */ Chain cali-INPUT (1 references) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere /* cali:i7okJZpS8VxaJB3n */ mark match 0x1000000/0x1000000 DROP ipencap-- anywhere anywhere /* cali:p8Wwvr6qydjU36AQ */ /* Drop IPIP packets from non-Calico hosts */ ! match-set cali4-all-hosts src
iptables 中还有表的概念,但从rule ==> chain 理解iptables 是最顺畅的。
引用
http://fishcried.com/2016-02-09/openvswitch-ops-guide/