简介
工作中常常用到Nginx 的location配置详解
Understanding Nginx Server and Location Block Selection AlgorithmsIn this guide, we will discuss some of the behind-the-scenes details that determine how Nginx processes client requests. Understanding these ideas can help take the guesswork(臆测、猜测) out of designing server and location blocks and can make the request handling seem less unpredictable.
Nginx logically divides the configurations (meant to serve different content) into blocks, which live in a hierarchical structure. nginx的内部结构是由核心部分和一系列的功能模块所组成。这样划分是为了使得每个模块的功能相对简单,便于开发,同时也便于对系统进行功能扩展。
The main blocks that we will be discussing are the server block and the location block.
- A server block is a subset of Nginx’s configuration that defines a virtual server used to handle requests of a defined type. Administrators often configure multiple server blocks and decide which block should handle which connection based on the requested domain name, port, and IP address. 通常一个server 配置对应一个域名
- A location block lives within a server block and is used to define how Nginx should handle requests for different resources and URIs for the parent server. The URI space can be subdivided in whatever way the administrator likes using these blocks. It is an extremely flexible model.
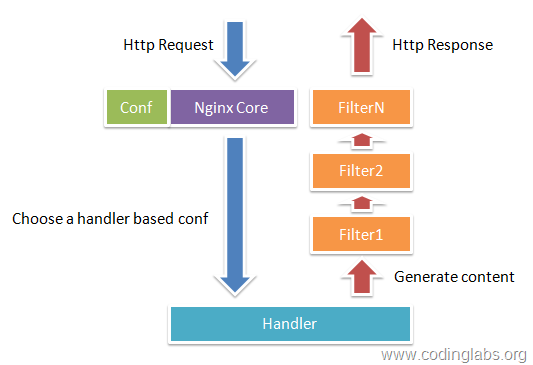
比较重要的模块
- nginx core
- nginx事件模块。估摸着,类似netty
- nginx http内核模块
你观察nginx配置文件,也可以知道nginx的配置项是按照这个顺序组织的。
nginx配置
nginx http内核模块配置项
http{
server{
server_name www.domain1.com
location /hello{
proxy_pass http://ip:port/...
}
localtion /world{
}
}
server{
server_name www.domain2.com
localtion{
}
}
}
用户在浏览器中键入http://www.domain1.com/hello
- 客户端将
www.domain1.com解析成ip - 访问
ip:80,www.domain1.com会作为host header设置在http请求中 - nginx 接到请求,根据Host header每个server的server_name进行匹配,选取server。
- 然后根据uri的剩余部分对localtion进行匹配
upstream负载均衡模块的配置项
http{
server{
server_name www.domain1.com
location /hello{
# 将server节点下的location节点中的proxy_pass配置为:http:// + upstream名称
proxy_pass http://backend1
}
}
upstream backend1 {
server 10.0.6.108:7080;
server 10.0.0.85:8980;
}
}
location 配置
Understanding Nginx Server and Location Block Selection AlgorithmsLocation blocks live within server blocks and are used to decide how to process the request URI (the part of the request that comes after the domain name or IP address/port). PS:终于明确的知道URI 说的啥了。
location optional_modifier location_match {
. . .
}
The location_match in the above defines what Nginx should check the request URI against. The existence or nonexistence of the modifier in the above example affects the way that the Nginx attempts to match the location block.
Syntax: location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }
| modifier修饰符 | 描述 | 优先级 |
|---|---|---|
| 无 | 前缀匹配 | |
| = | 精确匹配 | 如果找到,立即停止搜索 |
| ~ | 正则匹配,区分大小写 | |
| ~* | 正则匹配,不区分大小写 | |
| ^~ | 前缀匹配,不是带了~就是正则匹配了 |
如果找到,立即停止搜索 |
| / | 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到 |
几个原则:
- It is important to understand that, by default, Nginx will serve regular expression matches in preference to prefix matches. However, it evaluates prefix locations first, allowing for the administer to override this tendency by specifying locations using the = and ^~ modifiers. nginx 正则匹配优先于前缀匹配,但nginx 先进行前缀匹配再进行正则匹配,这样你可以在前缀匹配上 加 ` = or ^~
来改变nginx 的优先规则。PS:可以猜测下,nginx 最早没有= or ^~,只有前缀和正则匹配,正则优先级高。后来想给前缀匹配加一点例外,就有了= or ^~` - 前缀匹配 是匹配了最长的才算,所以即便当前location_match 匹配了,也不会立即结束。但正则匹配是一匹配就结束,所以对正则匹配location 来说,先后位置很重要。PS:更重要的是要知道,你加一个nginx映射,是会影响已有的映射的,加正则映射是高危操作,一个正则越”常见“(匹配范围越大),越危险,吃过亏的。
proxy_pass
proxy_pass 整体上是两种情况
-
If proxy_pass is specified without a URI, the request URI is passed to the server(下面的127.0.0.1) in the same form as sent by a client when the original request is processed, or the full normalized request URI is passed when processing the changed URI:
location /some/path/ { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; }proxy_pass 只指定了127.0.0.1 但没有指定 访问
127.0.0.1:80的具体地址,此时呢,http://domain/$path就会全部 对接到http://127.0.0.1/$path行 -
If the proxy_pass directive is specified with a URI, then when a request is passed to the server, the part of a normalized request URI matching the location is replaced by a URI specified in the directive:
location /name/ { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1/remote/; }http://domain/name/$other会被映射到http://127.0.0.1/remote/$other。 此处要注意,http://127.0.0.1和http://127.0.0.1/是不一样的,前者没有指定uri地址,后者则指定了/
假设用户请求为 http://192.168.1.1/proxy/test.html 那nginx 转发给服务器的路径是啥呢?
location /proxy/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1/;
}
|
http://192.168.1.1/proxy/test.html http://127.0.0.1/test.html |
location /proxy/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
}
|
http://192.168.1.1/proxy/test.html http://127.0.0.1/proxy/test.html |
location /proxy/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1/aaa/;
}
|
http://192.168.1.1/proxy/test.html http://127.0.0.1/aaa/test.html |
location /proxy/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1/aaa;
}
|
http://192.168.1.1/proxy/test.html http://127.0.0.1/aaatest.html |
如何自定义一个nginx模块
模块如何和nginx交互
配置文件中,http,server,location 在ngx_conf_file.h中有定义,对应NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF, NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF, NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF, NGX_HTTP_UPS_CONF.在模块的回调函数中,会将这些配置解析为struct,并作为参数传给module。类似于j2ee servlet的init(ServletContext context)等方法。
模块里面的配置,如gzip on,gzip其实是一个命令(command),on是它的参数。下面的所有均是如此,命令即是由模块提供的!包括下面的listen,server_name等等。location /说明当服务器收到/的请求时,执行哪些命令而已。
毕竟插件的运行是基于nginx的,所以,很多基本功能函数,比如为一个结构体申请空间、打日志等都会ngx_xx方法与之对应,以确保大部分操作都在nginx的管理和规范之下。
接口
其实类似于java,nginx core预留好接口(一系列回调函数)交给自定义模块实现。比较重要的是以下三个结构体(包括数据和函数):
- ngx_command_s,也叫ngx_command_t
- 上下文struct,根据模块不同而不同,比如ngx_http_module_t
- 模块本身ngx_module_s,也叫ngx_module_t
以ngx_http_module_t为例,结构中的所有成员都是指向回调函数的函数指针,这些函数在HTTP类模块初始化过程的不同阶段调用。
- *preconfiguration指针指向的函数是在解析配置文件中的http块前调用,
- *postconfiguration指针指向的函数是在完成http块解析后调用,
- *create_main_conf指针指向的函数在初始化http块之前调用,
- *init_main_conf指针指向的函数在初始化http块时调用,
- *create_srv_conf指针指向的函数在初始化server块之前调用,
- *merge_srv_conf指针指向的函数实现合并server块和http块中相同指令的配置,
- *create_loc_conf指针指向的函数在初始化location块之前调用,
- *merge_loc_conf指针指向的函数实现合并location块和server块中相同指令的配置。
模块的执行时机
与j2ee fitler不同,对于请求的处理,不是每个模块提供一个filter(request),然后所有模块排好先后,依次执行。
默认情况下,struct NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF, NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF, NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF, NGX_HTTP_UPS_CONF便可以完成一次请求的处理,我们要做的,就是在一系列初始化回调方法中,更改上述结构体的相关数据,比如替换原有的方法,来实现对数据的特殊处理。
对于ngx_command_s,以hello world nginx 为例
location /helloworld{
helloworld;
}
struct ngx_command_s {
ngx_str_t name;
ngx_uint_t type;
char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
ngx_uint_t conf;
ngx_uint_t offset;
void *post;
};
nginx在解析配置文件时,会调用set函数(此处赋值为下文的ngx_http_helloworld_setup)。我们在set函数中,替换掉NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF->handler,在ngx_http_helloworld_handler中,将返回的数据结构赋值为hello world。
char* ngx_http_helloworld_setup(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf){
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
clcf->handler = ngx_http_helloworld_handler; /* handler to process the 'helloworld' directive */
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
小结
熟悉Nginx,为Nginx编写插件(一)中提到:”为某个东西写插件,还不如说是要更加深入地了解这个东西呢”,在了解了nginx的一些基本原理后,能够更好地操作nginx配置文件。