简介
建议先看下前文 Kubernetes源码分析——apiserver
来自入口 cmd/kube-controller-manager/controller-manager.go 的概括
The Kubernetes controller manager is a daemon that embeds the core control loops shipped with Kubernetes. In applications of robotics and automation, a control loop is a non-terminating loop that regulates the state of the system. In Kubernetes, a controller is a control loop that watches the shared state of the cluster through the apiserver and makes changes attempting to move the current state towards the desired state.
那么在分析之初,便会有几个问题
- current state 和 desired state 从哪来
- 如何加载已有的各种controller
- 如何加载自定义controller
- 每个controller的存在形态是什么
- control loop 的存在形态是什么
- 自定义controller 与官方的controller 在实现上有哪些共通点
背景知识
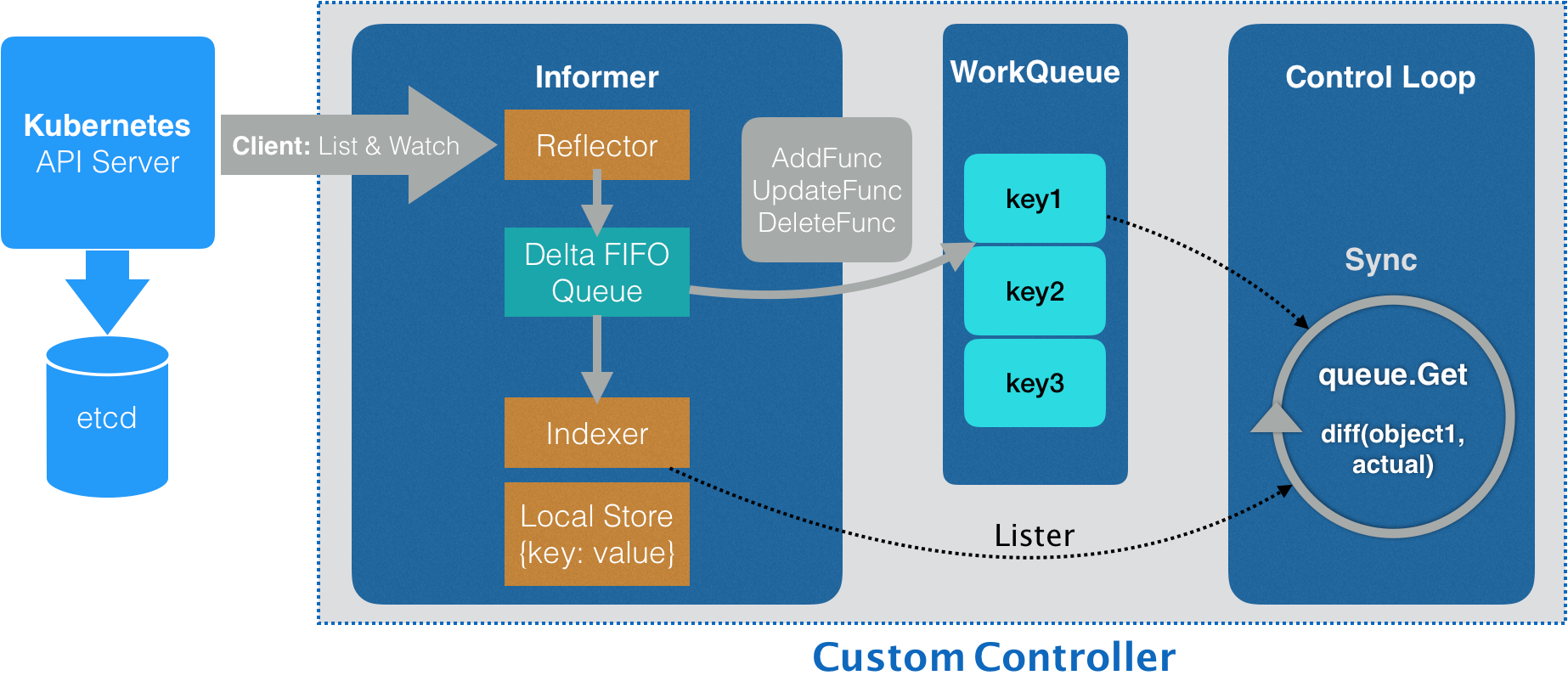
Controller 与 apiserver 的交互方式
Kubernetes源码分析——apiserver 提到Kubernetes CRD的实现,关于Custom Resource Controller的实现有一个很重要的点:Controller 与 apiserver 的交互方式——controller 与 apiserver 交互的部分已经被定好了,只需实现control loop 部分即可。
Kubernetes副本管理
本文以Deployment Controller 为例来描述 Controller Manager的实现原理,因此要预先了解下 Deployment Controller 的实现原理。
以扩展pod 实例数为例, Deployment Controller 的逻辑便是找到 关联的ReplicaSet 并更改其Replicas 的值
| Kubernetes object | 控制器逻辑 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | 控制 ReplicaSet 的数目,以及每个 ReplicaSet 的属性 | Deployment 实际上是一个两层控制器 |
| ReplicaSet | 保证系统中 Pod 的个数永远等于指定的个数(比如,3 个) | 一个应用的版本,对应的正是一个 ReplicaSet |
启动
cmd/kube-controller-manager/controller-manager.go
以启动DeploymentController为例

可以看到 启动一个goroutine 运行 Run 方法,Run begins watching and syncing.
control loop
Kubernetes找感觉 提到控制器的基本逻辑
for {
实际状态 := 获取集群中对象 X 的实际状态(Actual State)
期望状态 := 获取集群中对象 X 的期望状态(Desired State)
if 实际状态 == 期望状态{
什么都不做
} else {
执行编排动作,将实际状态调整为期望状态
}
}
那么实际在代码中长什么样子呢?我们先看下run 方法
外围——循环及数据获取
// Run begins watching and syncing.
func (dc *DeploymentController) Run(workers int, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer dc.queue.ShutDown()
klog.Infof("Starting deployment controller")
defer klog.Infof("Shutting down deployment controller")
if !controller.WaitForCacheSync("deployment", stopCh, dc.dListerSynced, dc.rsListerSynced, dc.podListerSynced) {
return
}
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go wait.Until(dc.worker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
<-stopCh
}
重点就是 go wait.Until(dc.worker, time.Second, stopCh)。for 循环隐藏在 k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/wait/wait.go 工具方法中,func Until(f func(), period time.Duration, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {...} 方法的作用是 Until loops until stop channel is closed, running f every period. 即在stopCh 标记停止之前,每隔 period 执行 一个func,对应到DeploymentController 就是 worker 方法
// worker runs a worker thread that just dequeues items, processes them, and marks them done.
// It enforces that the syncHandler is never invoked concurrently with the same key.
func (dc *DeploymentController) worker() {
for dc.processNextWorkItem() {
}
}
func (dc *DeploymentController) processNextWorkItem() bool {
// 取元素
key, quit := dc.queue.Get()
if quit {
return false
}
// 结束前标记元素被处理过
defer dc.queue.Done(key)
// 处理元素
err := dc.syncHandler(key.(string))
dc.handleErr(err, key)
return true
}
dc.syncHandler 实际为 DeploymentController 的syncDeployment方法
一次调协(Reconcile)
syncDeployment 包含 扩容、rollback、rolloutRecreate、rolloutRolling 我们裁剪部分代码,以最简单的 扩容为例
// syncDeployment will sync the deployment with the given key.
func (dc *DeploymentController) syncDeployment(key string) error {
namespace, name, err := cache.SplitMetaNamespaceKey(key)
deployment, err := dc.dLister.Deployments(namespace).Get(name)
// List ReplicaSets owned by this Deployment, while reconciling ControllerRef
// through adoption/orphaning.
rsList, err := dc.getReplicaSetsForDeployment(d)
scalingEvent, err := dc.isScalingEvent(d, rsList)
if scalingEvent {
return dc.sync(d, rsList)
}
...
}
// sync is responsible for reconciling deployments on scaling events or when they
// are paused.
func (dc *DeploymentController) sync(d *apps.Deployment, rsList []*apps.ReplicaSet) error {
newRS, oldRSs, err := dc.getAllReplicaSetsAndSyncRevision(d, rsList, false)
...
dc.scale(d, newRS, oldRSs);
...
allRSs := append(oldRSs, newRS)
return dc.syncDeploymentStatus(allRSs, newRS, d)
}
scale要处理 扩容或 RollingUpdate 各种情况,此处只保留扩容逻辑。
func (dc *DeploymentController) scale(deployment *apps.Deployment, newRS *apps.ReplicaSet, oldRSs []*apps.ReplicaSet) error {
// If there is only one active replica set then we should scale that up to the full count of the
// deployment. If there is no active replica set, then we should scale up the newest replica set.
if activeOrLatest := deploymentutil.FindActiveOrLatest(newRS, oldRSs); activeOrLatest != nil {
if *(activeOrLatest.Spec.Replicas) == *(deployment.Spec.Replicas) {
return nil
}
_, _, err := dc.scaleReplicaSetAndRecordEvent(activeOrLatest, *(deployment.Spec.Replicas), deployment)
return err
}
...
}
func (dc *DeploymentController) scaleReplicaSetAndRecordEvent(rs *apps.ReplicaSet, newScale int32, deployment *apps.Deployment) (bool, *apps.ReplicaSet, error) {
// No need to scale
if *(rs.Spec.Replicas) == newScale {
return false, rs, nil
}
var scalingOperation string
if *(rs.Spec.Replicas) < newScale {
scalingOperation = "up"
} else {
scalingOperation = "down"
}
scaled, newRS, err := dc.scaleReplicaSet(rs, newScale, deployment, scalingOperation)
return scaled, newRS, err
}
func (dc *DeploymentController) scaleReplicaSet(rs *apps.ReplicaSet, newScale int32, deployment *apps.Deployment, scalingOperation string) (bool, *apps.ReplicaSet, error) {
sizeNeedsUpdate := *(rs.Spec.Replicas) != newScale
annotationsNeedUpdate := ...
scaled := false
var err error
if sizeNeedsUpdate || annotationsNeedUpdate {
rsCopy := rs.DeepCopy()
*(rsCopy.Spec.Replicas) = newScale
deploymentutil.SetReplicasAnnotations...
// 调用api 接口更新 对应ReplicaSet 的数据
rs, err = dc.client.AppsV1().ReplicaSets(rsCopy.Namespace).Update(rsCopy)
...
}
return scaled, rs, err
}
调用api 接口更新Deployment 对象本身的数据
// syncDeploymentStatus checks if the status is up-to-date and sync it if necessary
func (dc *DeploymentController) syncDeploymentStatus(allRSs []*apps.ReplicaSet, newRS *apps.ReplicaSet, d *apps.Deployment) error {
newStatus := calculateStatus(allRSs, newRS, d)
if reflect.DeepEqual(d.Status, newStatus) {
return nil
}
newDeployment := d
newDeployment.Status = newStatus
_, err := dc.client.AppsV1().Deployments(newDeployment.Namespace).UpdateStatus(newDeployment)
return err
}