简介
背景
对于springboot项目,一开始是用java -jar 方式容器中启动,并作为容器的主进程。但测试环境,经常代码逻辑可能有问题,导致主进程失败,容器启动失败,进而触发marathon/k8s健康检查失败,进而不断重启容器。开发呢也一直抱怨看不到“事故现场”。所以针对这种情况,直观的想法是 不让java -jar 作为容器的主进程,进而产生一个在容器中运行多进程的问题。
但容器中运行多进程,跟 one process per container 的理念相悖,我们就得探寻下来龙去脉了。
从业界来说,虽然一个容器一个进程是官方推荐,但好像并不被大厂所遵守,以至于阿里甚至专门搞了一个PouchContainer 出来,美团容器平台架构及容器技术实践
此外要注意的是,一个容器多进程 在k8s 的Pod 概念下,要相机做出一定的调整。
为什么推荐一个容器一个进程?
stack exchange Why it is recommended to run only one process in a container? 有一系列回答
Run Multiple Processes in a Container 也提了三个advantages
理由要找的话有很多,比较喜欢一个回答:As in most cases, it’s not all-or-nothing. The guidance of “one process per container” stems from the idea that containers should serve a distinct purpose. For example, a container should not be both a web application and a Redis server.
There are cases where it makes sense to run multiple processes in a single container, as long as both processes support a single, modular function.
一个容器多个进程有什么风险
- 当PID1进程结束之后,Docker会销毁对应的PID名空间,并向容器内所有其它的子进程发送SIGKILL。
-
PID1进程对于操作系统而言具有特殊意义
- 操作系统的PID1进程是init进程,以守护进程方式运行,是所有其他进程的祖先,具有完整的进程生命周期管理能力。
- 如果它没有提供某个信号的处理逻辑,那么与其在同一个PID名空间下的进程发送给它的该信号都会被屏蔽。这个功能的主要作用是防止init进程被误杀。
- 当一个子进程终止后,它首先会变成一个“失效(defunct)”的进程,也称为“僵尸(zombie)”进程,等待父进程或系统收回(reap)。在Linux内核中维护了关于“僵尸”进程的一组信息(PID,终止状态,资源使用信息),从而允许父进程能够获取有关子进程的信息。如果不能正确回收“僵尸”进程,那么他们的进程描述符仍然保存在系统中,系统资源会缓慢泄露。
- 如果父进程已经结束了,那些依然在运行中的子进程会成为“孤儿(orphaned)”进程。在Linux中Init进程(PID1)作为所有进程的父进程,会维护进程树的状态,一旦有某个子进程成为了“孤儿”进程后,init就会负责接管这个子进程。当一个子进程成为“僵尸”进程之后,如果其父进程已经结束,init会收割这些“僵尸”,释放PID资源。
docker stop 对PID1进程 的要求
- 容器的PID1进程需要能够正确的处理SIGTERM信号来支持优雅退出
- 如果容器中包含多个进程,需要PID1进程能够正确的传播SIGTERM信号来结束所有的子进程之后再退出。
综上,如果一个容器有多个进程,可选的实践方式为:
- 多个进程关系对等,由一个init 进程管理,比如supervisor、systemd
-
一个进程(A)作为主进程,拉起另一个进程(B)
- A 先挂,因为容器的生命周期与 主进程一致,则进程B 也会被kill 结束
- B 先挂,则要看A 是否具备僵尸进程的处理能力(大部分不具备)。若A 不具备,B 成为僵尸进程,容器存续期间,僵尸进程一致存在。
- A 通常不支持 SIGTERM
所以第二种方案通常不可取,对于第一种方案,则有init 进程的选型问题
| 僵尸进程回收 | 处理SIGTERM信号 | alpine 安装大小 | 专用镜像 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sh/bash | 支持 | 不支持 | 0m | 脚本中可以使用exec 顶替掉sh/bash 自身 | |
| Supervisor | 待确认 | 支持 | 79m | ||
| runit | 待确认 | 支持 | 31m | phusion/baseimage-docker | |
| s6 | 33m |
一个容器多个进程的可能选择
自定义脚本
官方 Run multiple services in a container
systemd
CHAPTER 3. USING SYSTEMD WITH CONTAINERS
Running Docker Containers with Systemd
Do you need to execute more than one process per container?
supervisor
官方 Run multiple services in a container
Admatic Tech Blog: Starting Multiple Services inside a Container with Supervisord
使用
supervisord.conf
[supervisord]
nodaemon=true
logfile=/dev/stdout
loglevel=debug
logfile_maxbytes=0
[program:pinggoogle]
command=ping admatic.in
autostart=true
autorestart=true
startsecs=5
stdout_logfile=NONE
stderr_logfile=NONE
Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu
...
COPY supervisord.conf /etc/supervisor/conf.d/supervisord.conf
...
CMD ["/usr/bin/supervisord"]
runit
Run Multiple Processes in a Container
A fully powered Linux environment typically includes an init process that spawns and supervises other processes, such as system daemons. The command defined in the CMD instruction of the Dockerfile is the only process launched inside the Docker container, so system daemons do not start automatically, even if properly installed.
runit - a UNIX init scheme with service supervision
使用
Dockerfile
FROM phusion/passenger-ruby22
...
#install custom bootstrap script as runit service
COPY myapp/start.sh /etc/service/myapp/run
myapp/start.sh
#!/bin/sh
exec command
在这个Dockerfile 中,CMD 继承自 base image。 将myapp/start.sh 拷贝到 容器的 /etc/service/myapp/run 文件中即可 被runit 管理,runit 会管理 /etc/service/ 下的应用(目录可配置),即 Each service is associated with a service directory
这里要注意:记得通过exec 方式执行 command,这涉及到 shell,exec,source执行脚本的区别
Using runit for maintaining services
| 作用 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|
| runit-init | runit-init is the first process the kernel starts. If runit-init is started as process no 1, it runs and replaces itself with runit | |
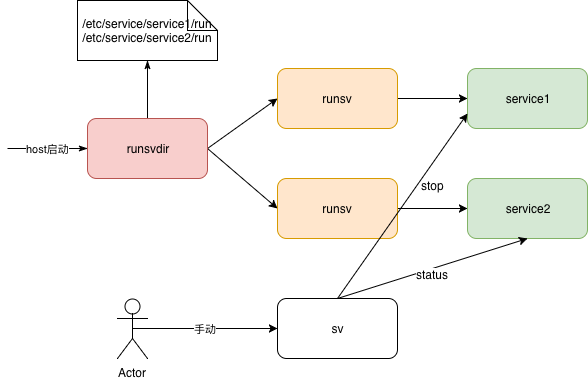
| runsvdir | starts and monitors a collection of runsv processes | 当runsvdir检查到/etc/service目录下包含一个新的目录时,runsvdir会启动一个runsv进程来执行和监控run脚本。 |
| runsvchdir | change services directory of runsvdir | |
| sv | control and manage services monitored by runsv | sv status /etc/service/testsv stop /etc/service/testsv restart /etc/service/test |
| runsv | starts and monitors a service and optionally an appendant log service | |
| chpst | runs a program with a changed process state | run脚本默认被root用户执行,通过chpst可以将run配置为普通用户来执行。 |
| utmpset | logout a line from utmp and wtmp file | |
| svlogd | runit’s service logging daemon |
runit 工作原理
s6
Managing multiple processes in Docker containers
Docker-friendliness image
与其在init 进程工具的选型上挣扎,是否有更有魄力的工具呢?
- docker 原生支持多进程,比如阿里的 pouch
- 原生支持多进程的 镜像
github 有一个 phusion/baseimage-docker 笔者2018.11.7 看到时,有6848个star。 该镜像有几个优点:
- Modifications for Docker-friendliness.
- Administration tools that are especially useful in the context of Docker.
- Mechanisms for easily running multiple processes, without violating the Docker philosophy. 具体的说,The Docker developers advocate running a single logical service inside a single container. But we are not disputing that. Baseimage-docker advocates running multiple OS processes inside a single container, and a single logical service can consist of multiple OS processes.
什么叫 ubuntu 对 Docker-friendliness?(待体会)
- multi-user
- multi-process
优雅的管理springboot 项目
回到文开始提到的问题:
phusion/baseimage-docker 的image 是基于ubuntu,笔者试着用alpine + runit + sshd 实现了一个简洁的base image,具体情况待实践一段时间再交流。
- 多进程方式,使得不管springboot 是否启动成功,容器都会启动成功
- 另外采取 措施监控 springboot 的健康状态,以决定是否 向该容器打入流量
- runit 正常会尝试不断重启,实际上往往因为代码的原因,启动一次就行了。因此启动springboot 的时候,先检查下 有没有
/etc/service/springboot/supervise(runsv将服务的状态保存服务对应在supervise目录中) 文件,若没有则是第一次启动。有则是第二次启动,写入/etc/service/springboot/down(down 告知runsv 停止该服务)
个人微信订阅号
